Types Of Training Programs For Workers
The design methodology on the lessons of foreign language Project-based learning - a comprehensive training method that allows to individualize the learning process, enables the student to exercise autonomy in planning, organizing and monitoring their activities. Project-based learning allows students to demonstrate independence in the choice of topics, sources, method of its presentation, and presentations.
The design technique allows an individual to work on a topic of greatest interest to each participant in the project, which will certainly entail an increased activity of a motivated student. He chooses an object of research for himself decides: whether to limit a textbook in English (just do a regular exercise), or read other books, set curriculum. However, children often turn to additional sources of information (for literature, encyclopedias), analyze, compare, leaving the most important and entertaining. Practical work on the project begins at the stage of 'discussion' and 'repetition' and becomes a harmonious part of the whole process of learning. One of the main features of the project activity, in our opinion, is the orientation towards a specific practical aim - a visual representation of the result, whether it be drawing, application or essay, or something else.
In the English-language training project method provides an opportunity for students to use language in situations of real everyday life, which undoubtedly contributes to better learning and retention of knowledge of foreign languages. Project work - the kind of work (preferably in groups) whose purpose is to prepare the final product in English - the album, giving information, etc. The purpose of this kind of work - to give student the opportunity to perform independent work, based on knowledge and language skills and knowledge acquired over a period of study topics. Project works are ideal for groups of different levels, since each task can be performed by students that have different levels of training. In the process of design students actually communicate among themselves and with the outside world in English. The practical aim of a project work may be based on improving various skills.
Some work requires more practice speaking, others more focused on the development of writing skills, and still others require the use of certain artistic abilities. Some tasks are more suitable for individual work, etc. to work in pairs or small groups. It is important to help students choose the tasks and methods of execution such that they feel most comfortable. To the question 'Why design work?'
Для психологов, педагогов, социологов и социальных работников / English for Psychology, Pedagogy, Social Studies, and Social Workers. Havryluk N., Pichkar O. English course for professional training of social workers. Файл формата zip. Размером 825,53 КБ. Содержит документ формата doc. Добавлен пользователем Чет 19:33. Отредактирован 07:01. Uzhhorod, 2000. [.] and Resource Training Programme, 2 Training Coordination Officers in support of all-job specific and technical training) (A/65/761, paras. 212 and 213). These training packages range from those conducted at the factory for a specific transformer type to those programs offered at the customer’s site for a specific job or general training requirement. Эти учебные пакеты варьируются от тех, которые проводятся на заводе-изготовителе для конкретного типа трансформаторов до тех программ, предлагаемых на территории заказчика для конкретной работы или общее обучение.
We give the following answer:. that motivates project work (Students write about themselves - their family, their house, their interests and preferences. Working on the project, students conduct a small research work on subjects of interest. The students actively involved during project work. Carrying out the project, students often something cut, paint over, write about something, looking for information in books, communicate with other people, are the illustrations - perhaps, make audio or video. Students at various levels and language development can implement their own project - large or small, simple or complex - and can be proud of him. For example, some students in the class may know the language weaker than others, but it would not interfere in the process of the project to identify skills to design or illustrate their work or find an original approach to presentation of the project).
that project work individually oriented (Preparing a story about your environment, in writing, students discover the importance of English and international languages. Once in the future, maybe they will tell a foreigner in English about his family, city or preferences. Work on this project helps them prepare to such events. Focusing on the theme that is studied in English, students have the opportunity to learn about the culture of English-speaking countries, and compare them with their views and thereby enrich their own understanding of other cultures). that project work has general value (Most modern school programs require that education contributed to the development of students in the initiative, independence, imagination, self-discipline, cooperation with other students and good research skills. The design work is a practical way of these educational purposes in class and after school).
Practical considerations Project work includes various activities. Students may have to move around the class, for example, ask other students or find information in reference books.
Of course, the class will then silence. But it is productive noise that will facilitate the task. Preparation, execution and presentation of the project takes much longer to implement than traditional tasks. But not all design work must be done in class. If the project is being prepared as an individual, the students can continue working on it at home.
Many students want to further work on a project to create such a work, whatever they can really be proud of. It is clear that most students will speak their native language during the project. It is natural and inevitable, and there needs to be recognized as a problem.
Index - the final result was formulated in English. Project work provides opportunities to use real translation - for example, English translation of leaflets, maps, interviews with family members, reference texts, written language. The beginning of project work The key to success of project work is good preparation and organization. For the project requires that the class had scissors, rulers, glue and large sheets of paper.
Students also have access to a small reference library where one could find a dictionary, grammar and atlas. Students should be encouraged to collect and bring in their own class materials: magazines, brochures, maps, postcards, etc., even if all that written language.
Teachers also need to collect such material. Students must learn to independently find information and seek assistance from the teacher only when they can not find the answer. Children must also learn to plan their actions and to decide what material they need to perform project tasks and where they can find them. Evaluation of the finished project Students always want to hear feedback about their project from the teacher. Essential that the students evaluated not only in terms of linguistic correctness. Teachers should observe how creative and innovative work is and how many efforts were made for its implementation.
It is important that teachers do not correct errors in the final version of the draft. This should be requested to prepare students to test and show the first draft of the project.
Thus, errors are found, and the final version of the draft will not patch. Examples of tasks for project work, most recently remembered me and my students:. 'Book of Weather' ('A weather book'). Children make cards, which draw a schematic of the different types of weather, are these cards in envelopes that are bonded to specific books or notebooks - the book forecast. 'During the lesson we orally find out what the weather outside with cards (students lay the appropriate card parties, and teacher on the board) and set out the description of weather in the books.
Projects ' Learning to learn' with practical ideas and tips on working language (the study of words, rules, work with dictionaries and manuals, reading the original literature, preparation for exams, etc.). The results of this work are issued in the form of vivid sights.

Questionnaires, interviews, research on the subject of the study.
На русском языке. Письменно своими словами изложите основное содержание текста I. Прочитайте текст. Опираясь на информацию текста, найдите Text B XI. Задайте к тексту 5-6 вопросов разного типа, отражающих его X. Переведите текст контрольной работы № 6 на русский язык. Основное содержание.
ЗАДАНИЯ К ТЕКСТУ: ответы на следующие вопросы: 1. What is the major purpose of employee orientation? 2.
What points are usually included into an employee formal orientation program? Name three of them you consider most important.
A. b. c. 3. What is the difference between the “on-the-job” and “off- the -job management training courses.?
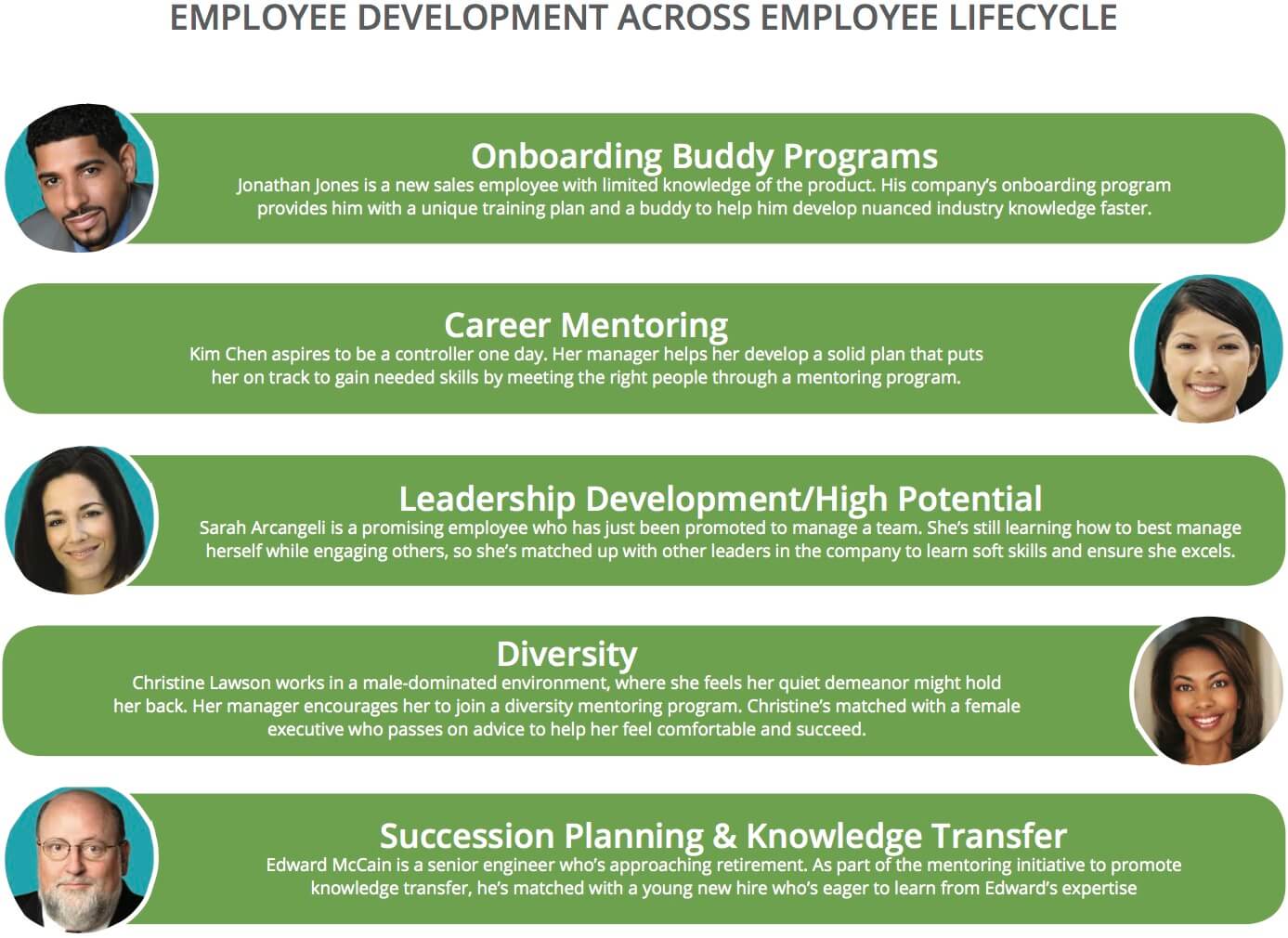
III. Задайте к тексту 6 – 7 вопросов разного типа. (1) Today’s forward-thinking organizations are recognizing that people are their most vital resource and an integral part for achieving increased productivity. Therefore, many firms are getting much more involved in continuing education and development programs for their employees. Career development is no longer just a system of promotions and occasional training programs. Rather, it is a long - term organizational strategy for assisting employees to optimize their skills and advance their education. (2) Training and development include all attempts to improve employee performance through learning.
One of these activities is employee orientation. The purpose of employee orientation is to inform employees of policies, practices, procedures and objectives of the organization. Orientation programs vary from quite informal, to formal schedules that have employees visit various departments for a day or more. Standard orientation program may cover: -history and general policies of the organization; -descriptions of products or services provided by the organization to the public; -the organization’s chain of command; -company safety measures and regulations; -human resources policies and practices; -compensation, benefits, and employee services; -daily routines and regulations; -introduction to the corporate culture; -organizational objectives. (3) The most fundamental employee training programs involve on-the-job training and off-the-job training. On-the-job training means that the employee immediately begins his or her tasks and learns by doing or watching others for a while, and then imitates them. Right at the workplace.
On - the - job training is obviously the easiest kind of training and can be effective where the job is easily learned. Off-the-job training develops a variety of skills and fosters personal development away from the workplace. It includes classroom, lectures, conferences, films, as well as workshops, tapes, reading programs, and the like. Some firms do such training internally and have elaborate training facilities.
Other firms assign such training to outside sources. Some supervisors apply to the so-called “vestibule training”. The term describes training in a classroom or away from the actual work area. It is done in schools where employees are taught on equipment similar to that used on the job. Such schools (oddly enough called vestibule schools) enable employees to learn proper methods and safety procedures before assuming a specific job assignment in an organization. For example, computer training is often completed in a vestibule school.
One of the faster-growing aspects of training is job simulation. Job simulation is the use of equipment that duplicates job conditions and tasks so that trainees can learn skills before attempting them on the job.
(4) Training is generally associated with operating employees, while development is associated with managerial personnel. Managers need different training than most employees. They need to be good communicators and especially need to learn listening skills and empathy.
They also need time management, planning, and human relations skills. Management development, then, is the process of training and educating employees to become good managers and then further develop their managerial skills.
Management development programs have sprung up everywhere, especially at colleges, universities, and private management development firms. Managers participate in various role-playing exercises, solve various management cases, and are exposed to films, lectures, and all kinds of management development processes. In some organizations managers are paid to take college level courses through the doctoral level.
(5) Most management training programs include on-the-job coaching and off-the-job courses. On-the-job coaching means that a senior manager will assist a lower-level manager by teaching him or her the needed skills and generally providing direction and advice. Such programs are only effective when the senior managers are skilled themselves and have the ability to educate others.
Светильник s0180/5 сборка. Off-the-job courses and training mean that managers periodically go to school or attend seminars for a week or more to hone their technical and human relations skills. Примечаниe: safety measuresмеры по технике безопасности on-the-job training обучение без отрыва от производства off-the-job trainingобучение с отрывом от производства foster (v)совершенствовать, благоприятствовать vestibule training производственное обучение simulation (n)моделирование, имитирование. Spring up(v)возникать, появляться coaching(n) обучение hone (v) совершенствовать, оттачивать.